
We are recruiting a couple of highly self-motivated graduate students who will work on Internet-of-Things (IoT) systems. Please, feel free to contact Prof. Kae-Won Choi (email: kaewonchoi@skku.edu) for more information.
Research Area
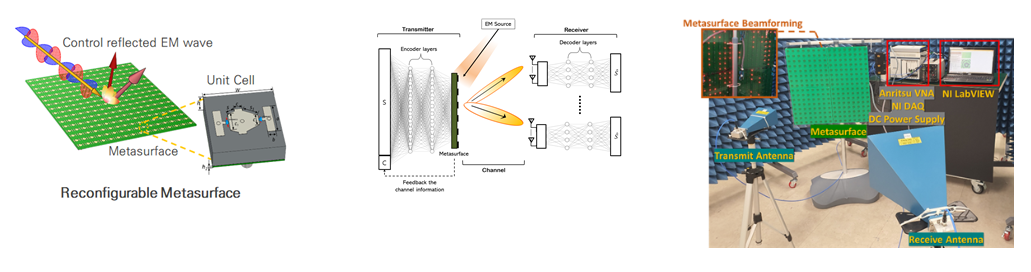
A study on mmWave communications based on reconfigurable metasurface
Overview
In this research project, we aim to develop a mmWave communications system based on reconfigurable metasurface. By adopting reconfigurable metasurface technology to ultra high frequency range communication technology, we can overcome inevitable limitations caused by using high frequency electromagnetic wave such as tremendous amount of path loss and shaded area due to the high straight forwardness characteristic.
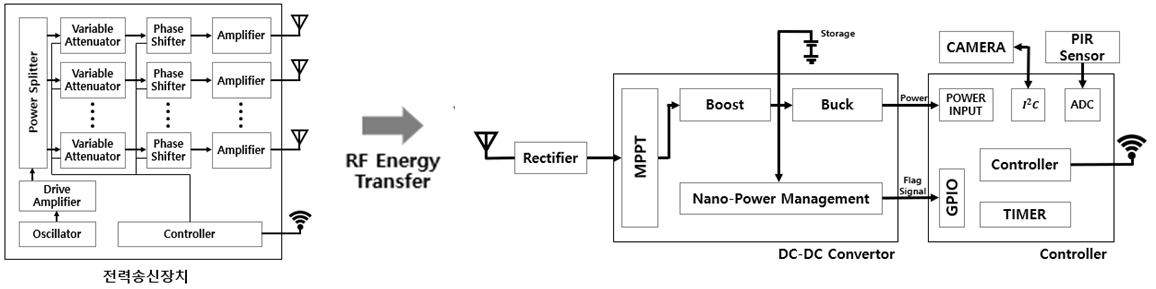
Energy Maintenance Wireless Power Camera System
Overview
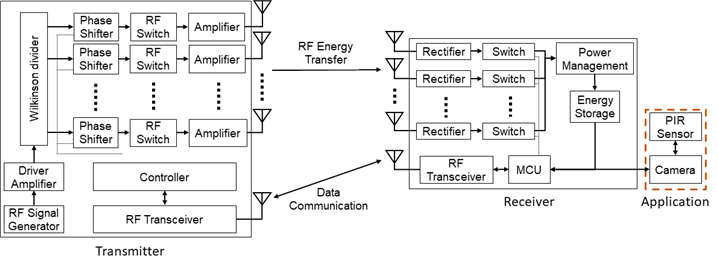
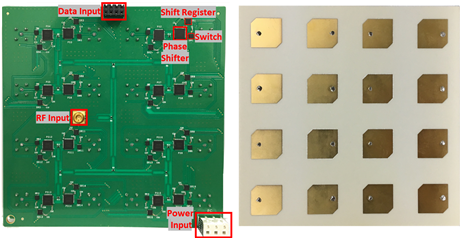
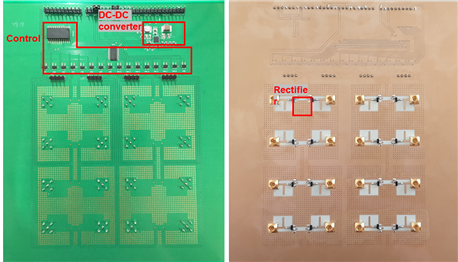
The Research proposes a system in which a wireless power camera that operates by being wirelessly powered and actively maintains energy. The power management includes not only transmission power control in the power transmission apparatus as the transmitting end but also control in the wireless power camera operating unit as the receiving end. For such control, the power transmitter and the wireless power camera operator may exchange control information through a transceiver.
The wireless power camera operating unit measures the remaining energy of the energy storage connected to the wireless power camera operating unit. When the residual energy is below a certain level, power is requested to the power transmitter through the transceiver. The power transmitter determines beamforming based on the position of the wireless power camera operating unit according to the request. The wireless power camera operating unit transmits photographing and data as motion is detected, and can actively request energy from the power transmitter based on the remaining energy. An object of the present research is to implement a fully wireless camera that can maintain the camera without replacing the battery in a place difficult to access through this.
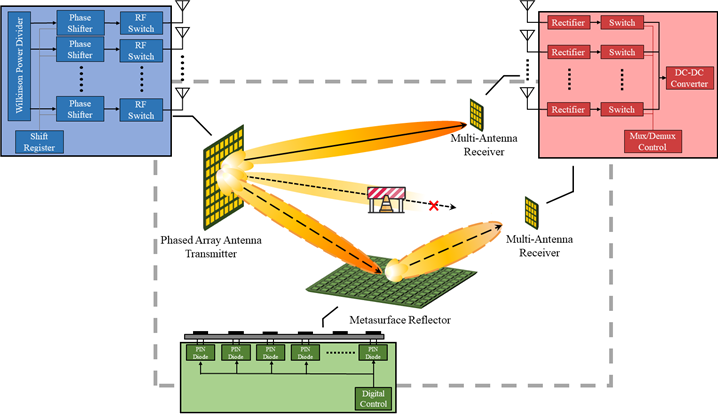
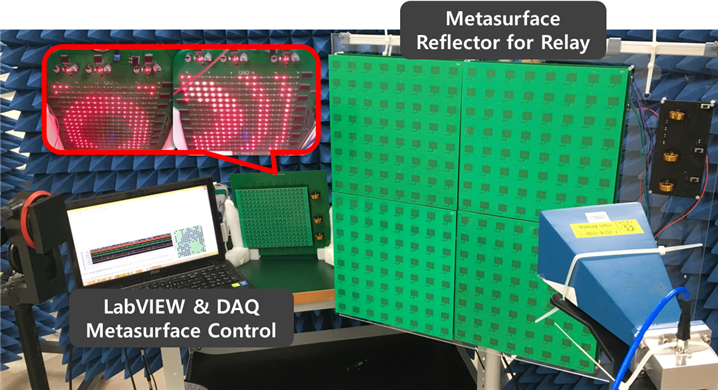
Multi-Antenna based Long-Range Wireless Power Transfer System with Reconfigurable Metasurface Reflector
Overview
The whole system is made up of phased array antenna transmitter, RF-DC convert circuits receiver and 1-bit coding metasurface reflector. To tackle its low power transfer efficiency between transmitter and receiver, which is the foremost obstacle of radio frequency (RF) based WPT, we have implemented high-efficiency microwave beam synthesizing with multiple antennas. Inevitable shaded area due to the various kinds of obstacles between transmitter and receiver has been solved by deploying reconfigurable metasurface near the shaded area. In the case that transmitter detects obstacle in the middle, energy beam from the transmitter would be steered to metasurface and then by converting the phase of incident electro-magnetic waves of each cell in metasurface, transmitted power can be focused to receiver as well. With proposed convergent power transfer algorithm that handles all hardware components at the same time, optimized power transfer efficiency can be achieved regardless of whether the obstacle detected or not.
Development of GHz microwave energy charging system for smart IoT devices
Overview
Microwave energy charging system has been developed aiming to introduces a new alternative and ready to be commercially used long-range wireless charging devices. Unlike the near-field wireless charging commercial product, (e.g. wireless phone charger), proposed system utilize the property of electromagnetic wave to wirelessly transfer the energy from the far distance. Besides that, with the implementation of massive MIMO technology, the power transfer efficiency and the operational range can be significantly improved by using beamforming technique implemented on the this system.
5G Beamforming
Overview
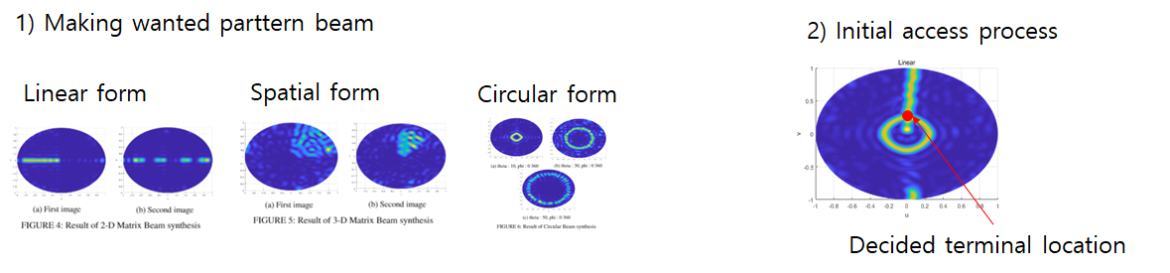
In a communication system utilizing beamforming, a beam alignment process is essential, and the overhead in this process is significant. In the case of A6G (Above 6GHz), more than 1000 beams are used. In order to satisfy various requirements of 5G, efficient beam alignment method is required in each scenario, the beam must be electrically steering In the direction of the terminal belonging to the cell, interference should be minimized through nulling. That is, a beamforming technique is needed to quickly find a terminal device where it may be located, start communication by aligning the beams, track movement well, and quickly recover when a communication link is broken due to surrounding conditions. We have optimized the algorithm using the Gradient Descent method so that it has various directivity and nulls and a radiation pattern of various beam-widths.
Challenge
We propose a method of adjusting only the phase of the feed signal by optimizing it with the objective function and computation process. We propose a beam synthesis method that can be effectively used in a communication system with a lot of limitations, and propose an initial access method of a millimeter wave communication system utilizing a planar array antenna using a synthesized beam.
Process
In order to effectively utilize the beam, research for forming various beams through beam synthesis is required. And initial access process is introduced by using several beam form to shoot the optimum beam.
Beam Avoidance for Human Safety in Radiative Wireless Power Transfer
Overview
The research proposes a beam steering algorithm to formulate the optimal phased antenna array weight that maximizes the received power on the target (IoT device) and at the same time maintains the amount of radiated microwave power toward human body below the recommended exposure limit. The research is motivated by the scientific studies about the human health risk that could be caused by microwave radiation exposure (e.g., heart disease, burns, skin cancer, etc).
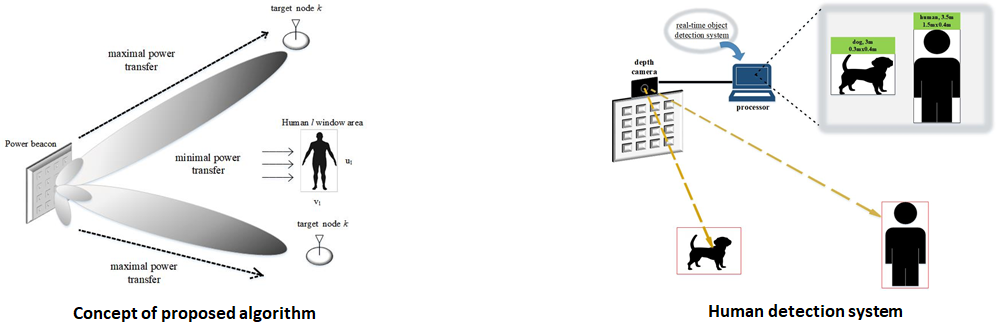
Challenge
In this research, the information of the exact location of human body is required to apply the algorithm to the system. Therefore, by incorporating a depth camera which utilizes the sensing technology based on human stereo vision with a deep learning-based real-time object detection system, the human presence can be detected, the distance from the power beacon to human body can be measured, and the window size of detected object can be obtained.
Process
The proposed algorithm has the main advantage to assure the use of RF radiated energy in wireless power transfer environment complies with the limit of human exposure to the microwave energy, which is regulated by communication international commission. The proposed algorithm can be easily applied and adapted to the receive power-based wireless power transfer employing a large number of antenna.
Study on Frequency Sharing Algorithms Based on Radio Wave Environment Information Using Machine Learning
Overview
Today, as the use of communication devices increases, a high-density network environment has also increased, and thus limited channel resources must be efficiently used. Since the existing fixed algorithm was developed to be used in the overall communication environment, there is a limit to the performance improvement over a certain level in the actual environment. If a communication algorithm using a reinforcement learning model is used, it is possible to maximize the use of channel resources by learning the data of the current environment, and to find a communication algorithm optimized by itself according to the changing environment.
Challenge
Therefore, in this study, we implement a frequency sharing environment simulator and develop a reinforcement learning model that optimizes communication algorithms according to the changing environment using the simulator.
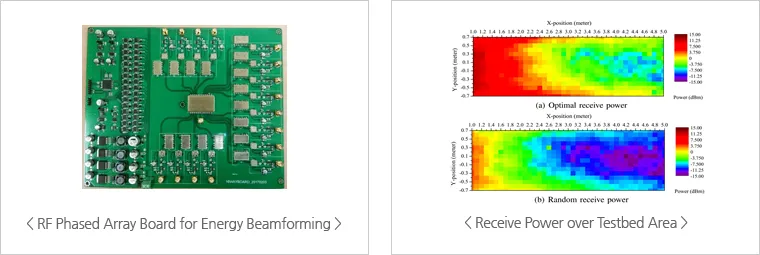
Wireless Power Transfer for Communication Networks
Overview
In this research topic, we study the radio frequency (RF) power transfer technique that makes use of an electromagnetic (EM) wave as a medium for carrying power. Differently from other wireless power transfer techniques (e.g., inductive coupling and magnetic resonant coupling), the RF energy transfer technique enjoys an advantage of longer energy transfer distance compared to other competing technologies thanks to the characteristics of the EM wave. Especially, we study a multi-antenna wireless-powered sensor network (WPSN), in which a power beacon wirelessly transfers electric energy to a sensor node via an EM wave.
SDR Development based on Ultra Dense Network
Overview
The ultra-dense network (UDN) is a next generation communication technology that can maximize spectral efficiency per unit area by simultaneously transmitting and receiving information through the same spectrum to multiple terminals through cooperative communication between a plurality of base stations arranged at very high density. In this research, we design UDN test bed based on software defined radio (SDR) platform to improve spectral efficiency of UDN structure in ultra high density environment and verify UDN core technology.
Challenge
We can modify the parameters such as modulation order, transmit power, and basis vector size, etc. in the top-level VI of the LabVIEW code and check the performance metrics such as bit-error rate (BER), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), channel gain, and signal constellation of each receiver. We have conducted experiments that measure these performance metrics according to various parameters.
Process
And one of the many challenges in the development and evaluation of these wireless systems is testing and verification. Therefore, the radio system must be tested to ensure specified requirement. But field tests are expensive, time-consuming, and difficult to repeat. Simulation can overcome these problems, but ultimately it is limited to accuracy or excessive running time. One way to compensate for these limitations is the real-time HIL channel emulation. This can compensate for the gap between simulation and field testing. A good channel emulator can test a wireless system in repeatability, high accuracy, and various network scenarios.
RF Wireless Power Transfer
Overview
RF Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) is a technology that enables wireless power transfer through the use of electromagnetic (EM) waves. Unlike magnetic WPT, which has a very short working distance, RF WPT can deliver wireless power to target devices located tens to hundreds of meters away. RF WPT has the potential to revolutionize the way we power electronic devices, making it possible to charge devices without the need for cables or batteries.

Challenge
One of the major challenges of RF WPT is achieving high power transfer efficiency over long distances. Non-focused radiation scatters microwave energy towards directions other than the target receiver, which makes it unsuitable for WPT application. Focused radiation, on the other hand, can focus a sharp microwave beam on the receiver to maximize power transfer efficiency.
Process
EM waves can be utilized for both data communication and power transfer. In RF WPT, a transmitter emits microwave energy towards the receiver, which then converts it into DC power using a rectifier. To achieve high power transfer efficiency, focused radiation is used to ensure that the microwave beam is directed towards the receiver. This enables the receiver to harvest a significant amount of power even from a long distance.
Cell-Free MIMO
Overview
Cell-Free MIMO is a wireless communication technology that provides simultaneous service to multiple users across a wide area, without clearly defined cell service boundaries. In contrast to conventional cellular communication, it uses a user-centric cell with protected UEs. This technology allows a cluster of nearby APs to be assigned to each UE, with multi-antenna APs and UEs assumed.
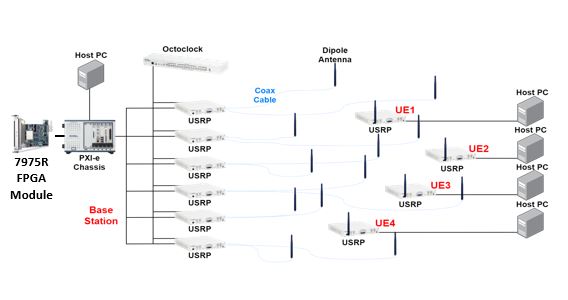
Challenge
The main challenge of Cell-Free MIMO technology is to maintain a set of “protected UEs” for each cell and minimize interference to them. The system also requires real-time exchange of information and calculations between base stations, which presents significant computational and architectural challenges.
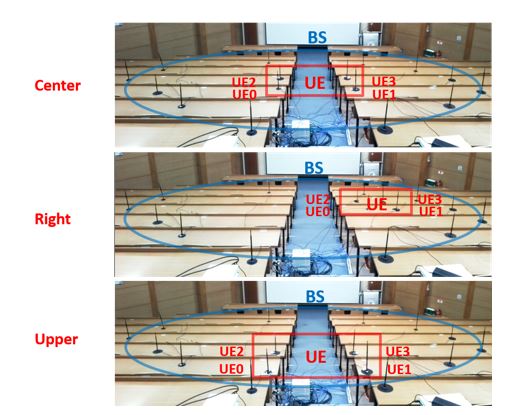

Process
Cell-Free MIMO technology is designed for distributed CPU, which means there is no dedicated hardware for CPU. Instead, each AP retains the capability of CPU so that all APs have an identical architecture. Each cell has a primary AP and others are called secondary APs. The primary AP performs high PHY signal processing and distributes the data stream to secondary APs. It also gathers channel information and computes the precoding matrix. This technology assumes multi-layer communications, and downlink OFDM communications are used.
6G Sub-THz
Overview
The sub-THz band has the potential to provide ultra-high-speed communication due to its wide bandwidth. However, this band is challenging due to the high attenuation, propagation loss, and hardware constraints. Researchers are working on exploring the sub-THz channel's characteristics, including reflection, diffraction, and transmission, to improve the transmission performance.
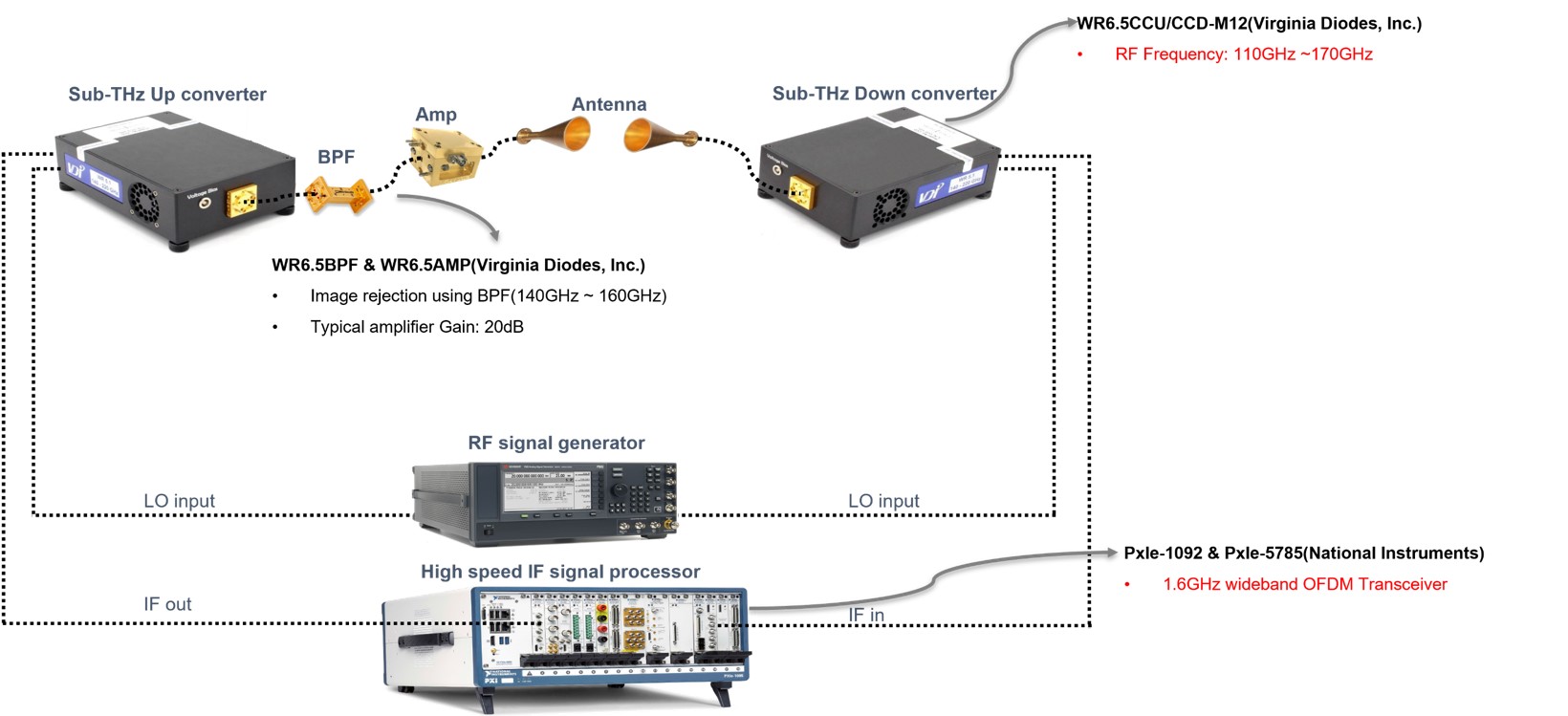
Challenge
One of the main challenges in sub-THz communication is the hardware limitation of the transceiver due to the high operating frequency. Line-of-sight (LoS) MIMO and hybrid beamforming technology have been proposed to overcome the hardware constraint and achieve better channel capacity. Moreover, RF impairments such as Phase noise, which affects the sub-THz band's transmission quality, are being compensated through various methods.
Process
Researchers are setting up sub-THz testbeds to observe and analyze the sub-THz band's RF impairments, such as Phase noise. Real-time compensation algorithms are being developed to improve the communication quality in the sub-THz band. Additionally, researchers are working on developing new techniques to utilize the sub-THz band more efficiently, which will be useful in the design of the next-generation wireless communication system.
Through-Wall MIMO Radar
Overview
Through-Wall MIMO Radar is a technology that allows for the collection of information about objects and people located in the space behind a wall or obstruction that blocks the line of sight. By using MIMO technology, which utilizes multiple antennas to simultaneously transmit and receive signals, a more accurate image of the target can be generated. The radar measures time delay and phase shift of reflected signals to determine the location, size, and movement of the object or person being detected.
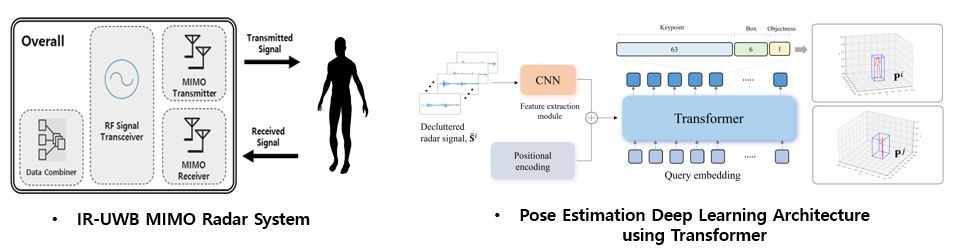
Challenge
In this research, an IR-UWB MIMO Radar system is configured with Multi-Input, Multi-Output (MIMO) technology on the Impulse Radar Ultra-Wide Band (IR-UWB) sensor. A large amount of RF signal data is collected for many people and various postures.

Process
The research focuses on RF signal-based pose estimation deep learning model, which applies collected RF signal data to a feature extraction module. The posture of a person located in an invisible space is estimated using Transformer, an attention-based deep learning model. This research can have significant implications in fields such as surveillance, rescue operations, and security.
Integrated Sensing and Communication
Overview
ISAC technology is based on the fact that both wireless communication and radar sensing areas use electromagnetic waves. We are researching the integration of communication and sensing at the millimeter wave (mmwave) and sub-THz band, where communication uses a relatively low frequency band and sensing uses a high frequency band that can obtain high resolution.
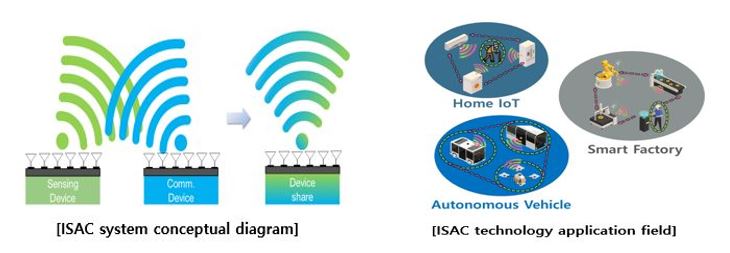
Challenge
As next-generation wireless communication bands are moving towards high frequency bands such as mmwave and sub-THz, integration research in this band is accelerating. We believe that our research can contribute to the development of ISAC technology, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs in the wireless communication system.
Process
Our research focuses on the development of Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) technology, which simultaneously performs communication and sensing using electromagnetic waves. This technology offers increased efficiency of radio frequency (RF) resources and reduced costs due to hardware sharing.In summary, ISAC technology is a promising approach that can offer significant benefits for both communication and sensing applications by integrating them into a single system. Our research aims to explore the full potential of this technology and to develop new methods to enable its widespread adoption.
AI-Based Spectrum Access
Overview
The rapid growth of wireless communication technology has led to an increasing demand for efficient utilization of wireless resources. Our research focuses on developing artificial intelligence-based spectrum access technology that can optimize WiFi resource utilization efficiency while protecting existing wireless stations in the 6 GHz.
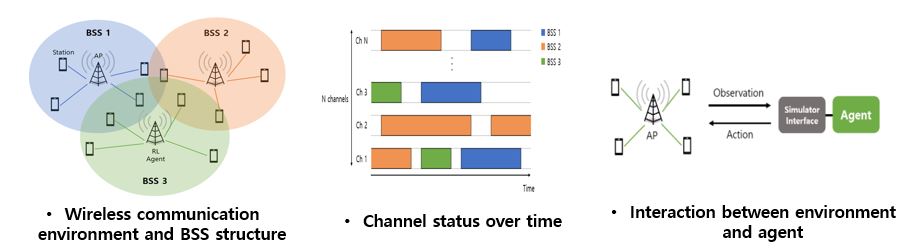
Challenge
To achieve this goal, we analyze the 802.11ax network technology and the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) transmission method in existing Media Access Control (MAC). We also investigate the technologies and requirements such as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), channel bonding, preamble puncturing, and Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO).
Process
We have developed an 802.11ax based communication simulator and agent that can be implemented in the form of Discrete Event Simulation (DES). We have created a user-friendly interface using Python and visualization tools to aid in the simulation process.Moreover, we have created reinforcement learning models using value-based algorithms such as Deep Q-Network (DQN), Double DQN (DDQN), and Rainbow DQN, as well as policy-based and actor-critic algorithms such as REINFORCE, Advantage Actor-Critic (A2C), and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO).
Bio Signal Processing(EMG, EEG)
Overview
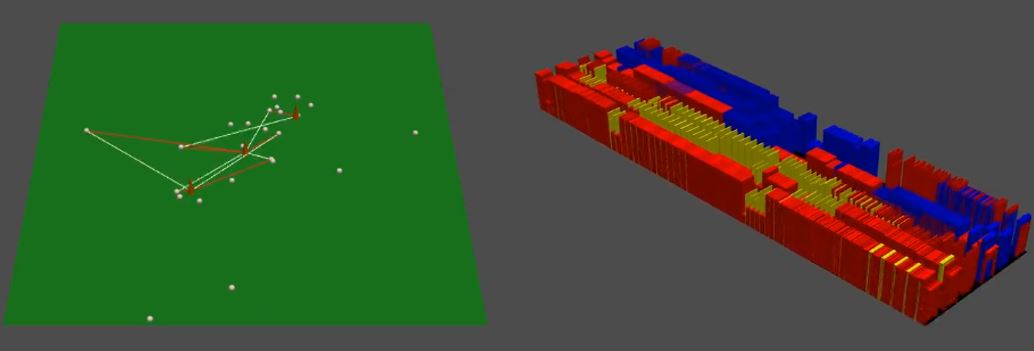
Bio-signal processing is a field of study that involves the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of signals produced by biological systems. Our research focuses on the processing of bio-signals, specifically electromyography (EMG) and electroencephalography (EEG), to estimate human behavior and movements.
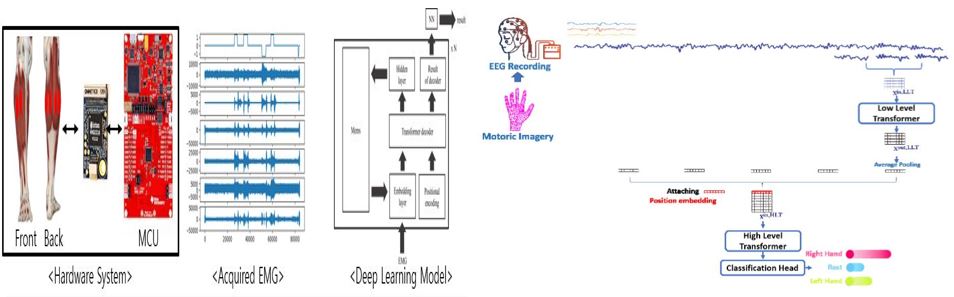
Challenge
We have developed a lower-limb EMG acquisition system that collects EMG signals continuously from a single channel. We have optimized the bio-signal acquisition system for both wired and wireless communication, allowing for flexibility and ease of use.
Process
Using deep learning networks, we analyze the collected EMG signals to estimate motion and control real-time avatars in the UNITY environment. Our research also involves studying the brain-computer interface, where we decode brain signals into motor imagery intentions. We utilize a public motor imagery dataset from EEG and classify the data using deep learning with a hierarchical transformer network.
Capacitive Touch Screen
Overview
Capacitive touch screen technology has become an integral part of modern digital devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. The ability to sense the presence and location of a touch through a change in capacitance has made capacitive touch screens a preferred choice over resistive and other types of touch screens.
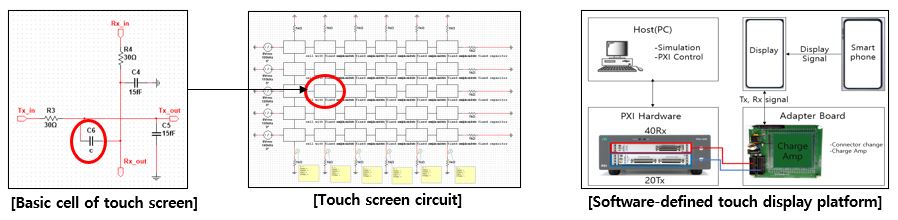
Challenge
Our research focuses on the implementation and improvement of touch screen panels using capacitive touch screen technology. We aim to develop a high-performance touch screen panel that can accurately detect multiple touch points and provide a smooth and responsive touch experience.
Process
To achieve this goal, we have developed a technique that includes Tx and Rx electrodes to detect the touched points by measuring the capacitance changes. We also represent the touched basic cell with mutual capacitance for simulation purposes.Furthermore, we have developed a software-defined touch display platform that includes 20 Tx electrodes and 40 Rx electrodes. We utilize PXI system-linked DAC and DAC modules to control the mutual capacitance of multiple cells, allowing us to implement multi-touch situations. We have combined the implemented touch screen panel with the PXI system, providing scalability to operate on FPGA and CPU.